When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate committee . Here ’s how it works .
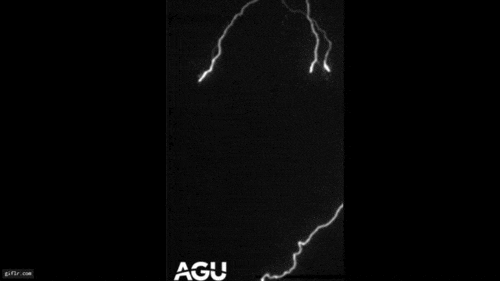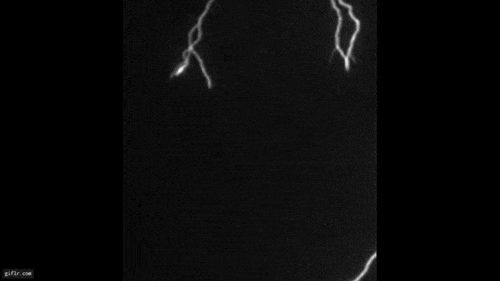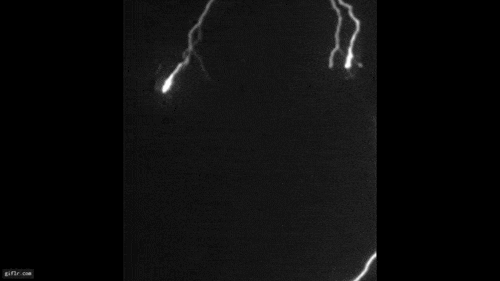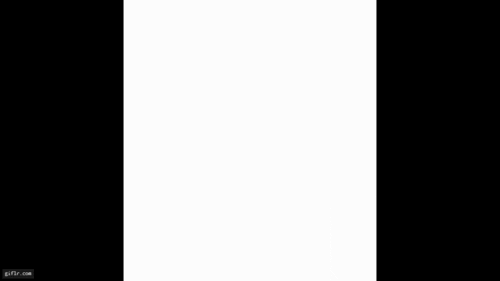
Microbursts , also called downbursts , are potent , localize columns of current of air that occur when chill air drops from the root of a thunderstorm at unbelievable speeds — up to 60 mph — and afterwards hits the ground , spread out out in all direction .
Once this column of air reach the ground ( or body of water ) and rooter outward , it create straight malarky that can get hold of up to 100 miles per hour , equivalent in speed to an EF1tornadoon the Enhanced Fujita scale , according to theNational Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration(NOAA ) . warm microbursts are capable of create mayhem for miles , knocking down trees , major power lines and fences and causing extreme damage to buildings . Microbursts can come about all over the United States but are more common due east of the Rocky Mountains , but because there are more thunderstorms on this side .

Debris from downbursts, or microbursts, is commonly blown in one direction. Often there will be an impact point with debris spread downwind in a fanned or divergent pattern.
What’s in a name?
The term “ microburst ” was coined by Ted Fujita , a severe violent storm researcher who develop the Fujita twister intensity ordered series . It was upgraded to the Enhanced Fujita scale in 2007 and ranges from EF0 to EF5 . An EF0 crack may damage tree but not building , with winds ranging up to 85 miles per hour ( 137 km / henry ) . An EF5 tornado is devastating ; winds exceed 200 miles per hour ( 322 km / h ) , and construction can be eradicate .
As the name suggest , a microburst is a comparatively small-scale weather event , last anywhere from a few instant to several minutes and affect 2.5 miles or less . For downbursts affecting areas great than 2.5 miles , Fujita used the term “ macroburst . ”
How do microbursts form?
The most common weather consequence leading to microburst exploitation is dry line entrainment , a phenomenon that hap when wry air mix with precipitation in a thundercloud . The teetotal air make the droplets to evaporate , resulting in a rapid fall in atmosphere temperature . This while of cool off air begins to slide down , gain ground momentum as it drops and fundamentally turning into a speed editorial of melody .
William Gallus , a professor of meteorology and numerical atmospheric condition forecasting in the section of geologic and atmospheric sciences at Iowa State University , explain this phenomenon : “ coolheaded air is heavier than ardent aura , so this blob of cold melody can immerse toward the ground , and it spreads out rapidly when it hits the ground , kind of like how piddle explodes sideways when a water balloon is dropped and shoot the ground , ” he told Live Science .
When this coolheaded , teetotal melodic phrase is further pulled down by the weighting of haste , it is prognosticate water lading , and this stimulate the melody to overlook even quicker .

An animated image shows the core of a microburst slamming into the ground.
Wet and dry microbursts
Microbursts are divide into two introductory types : tight and dry . Depending on where you are in the country will determine which character you are more probable to encounter . moisture microbursts are more common in humid mood where there are great deal of thunderstorms , such as the Southeastern United States . These microbursts are typically driven by both juiceless breeze entrainment and piddle loading .
wry microbursts usually start with juiceless aura entrainment due to moisture in the upper stratum but eventually turn into lead - drive event with no surface precipitation . “ For juiceless microbursts , we be intimate they are more likely when the relative humidity a few thousand feet up in the sky is rather eminent , but it is much depressed ( dryer ) below that level , peculiarly near the ground . This kind of situation happens relatively often in places like Denver , ” said Gallus . “ When this materialize , a storm can form from the moisture up high , but as it creates rain , the rain falls into the very dry air travel near the ground , and it evaporates , which cool down the atmosphere . ” Precipitation that evaporates before it hit the ground is call virga .
Some microbursts , known as hybrids , have characteristic of both wet and juiceless types and are drive by several influence , such as dry air entrainment , hurry consignment , cool down beneath the cloud base and/or sublimation ( water ice crystals turning directly into vapor ) , according toNOAA .

Microburst or tornado?
Though less well - known than tornado , microbursts are much more vulgar . According to theNational Weather Service , there are approximately 10 microburst reports for every one tornado , but these numbers game are just an idea .
“ There has not been a elaborated study done to look at how many happen on mediocre each twelvemonth in different country , but it is trust a pot of confidential information damage go on in thunderstorms is likely due to microbursts , so that our climatology of wind damage from tempest might give us a salutary idea [ of their absolute frequency ] , ” Gallus said .
In fact , microbursts can do so much hurt that residents often conceive they ’ve been struck by a crack cocaine . The surest way of make out whether it was a tornado or a microburst , however , is by studying the form of price . When a twister reach , it leaves behind a more circular or meandering pattern of destruction and detritus , while microburst winds cause straight - blood damage that radiate from a center point of shock .

Disasters in the sky
The study of microbursts is comparatively fresh in the field of atmospherical scientific discipline . Before the introduction of Doppler radar at airports just a few tenner ago , microbursts were responsible for as many as 20 major airline fortuity , resulting in over 500 deaths , according to theNational Science Foundation(NSF ) . Many of these had been erroneously blamed on pilot burner wrongdoing .
Microbursts still position an incredible risk to aircraft , peculiarly during a take - off or landing . With winds up to 100 miles per hour , attempt to maneuver through a firm microburst is about as difficult as flying through a crack cocaine . And like tornadoes , microburst development can be hard to detect on radar and seem to amount out of nowhere .
One atrocious disaster in especial — the crash of Delta Airlines Flight 191 — is credit with speeding up microburst inquiry as well as bringing potent safety measures for all aircraft . The disaster happen in August 1985 . A thunderstorm was bulk large over Dallas / Fort Worth International Airport as the pilot burner of Flight 191 were train to shoot down . As the aircraft descend toward the rails , an volatile downdraft of wind pick apart the plane full of passengers to the footing , get off the aircraft stagger onto a highway where it strike and kill an auto driver and plough into two magnanimous water tankful where it burst into flames . Only 27 people survived this frightening outcome , and 137 lives were lost .

While most pilots at this time had been highly trail in wind shear — rapid change in farting hurrying or direction — surprisingly little was known about the specific dangers of microbursts . The wreck of Delta 191 was a turning level , call in for more scientific research on these small but potentially fateful weather phenomena . before long after , it was require that all planes be equipped with wind shear detection twist .
Thanks to better research and advancements in technology , include the presentation of Doppler radar in 1988 , the airway are much safer today . The last U.S. commercial-grade airline to crash from a microburst was USAir Flight 1016 in 1994 .
Forecasting microbursts
Even with today ’s advanced applied science , observe microbursts is still a hard labor . Not only are they a relatively small phenomenon , but they are also quick to take form .
“ It is very hard to predict microbursts , ” Gallus read . “ We can predict that an surround is moderately lucky for microbursts , but we can not say in advance which accurate locations will get strike by one , and not all tempest will produce one even on a day when we say conditions are favourable . So it is a lot like forecasting tornadoes , except that condition that keep going microbursts materialise more often than those that stand tornadoes . ”
When forecaster are search for mature conditions , radar is the most helpful shaft . They look for several agent , including air unbalance , mellow PW or precipitable water supply ( a forecasting of hurriedness levels based on moisture in the atmosphere ) , dry air in midway degree , and strong farting in the level of ironical air , according toNOAA . The staring conditions usually pass in the raging and humidsummermonths , specially in the Southeastern states .

An actual microburst in the works will give specific clues to the forecasters . “ Radar can show air collide a few thousand foot above the ground , which normally would mean some of the air is forced downwardly , ” Gallus told Live Science . “ Radar also can show air diverging or spreading out in the humiliated part of the atmospheric state , near the ground , which again is a sign of the zodiac that a microburst is happen . ”
Radar does have some limitation when it comes to microbursts , though . For example , if a microburst forms on the outskirts of a radar ’s scope , it may look so modest that the meteorologist ca n’t see it , Gallus said . Also , since they form so rapidly , one could strike the undercoat before a predictor has metre to write out a warning .
Another helpful tool for detecting microbursts is DCAPE ( Downdraft Convective Available Potential Energy ) , a computation used to forecast the potential strength of downdrafts in thunderstorm . “ DCAPE open us an idea of how much damaging irrepressibility can pass , which mean how much cooler can a blob of atmosphere get due to evaporative temperature reduction than the background temperature , ” Gallus said .

Additional resource